electronics-journal.com
01
'24
Written on Modified on
PATH TO 6G: ENVISIONING NEXT-GEN USE CASES FOR 2030 AND BEYOND
Today, the early vision for 6G is starting to emerge. The next-generation mobile platform is targeted to bring a large technology leap for 2030 and beyond.
www.qualcomm.com

6G is the next cellular generation building on 5G learning and technology foundation. It will fuel innovations that can enable new and enhanced use cases in the decade to come. Today, the early vision for 6G is starting to emerge. The next-generation mobile platform is targeted to bring a large technology leap for 2030 and beyond. 6G will be more than a new radio design, it is envisioned to be an innovation platform of synergistic technologies, including AI, sensing, security, green networks/devices, and more, which will enable sustained expansion of the connected intelligent edge.
At Qualcomm, we are driving longer-term research to lead the 5G Advanced evolution and establish the technical foundation for 6G.
6G goals and drivers
At a high level, here are the key goals and drivers for the 6G innovation platform to achieve in the next decade and beyond:
- Economics growth: 6G is poised to unlock novel revenue streams, and enable a plethora of new devices, services and deployments. Although it may be premature — or even naïve — to quantify its impact at this point of time, 6G is anticipated to be a significant driver of sustained global economic growth, fostering industry innovations and transformations.
- Technology advancement: While innovation is a continuous process, commercializing major breakthroughs in core technologies efficiently must wait for a generational transition, when a blank-slate design can be introduced. 6G can align ecosystem investments to bring the next big leap in wireless technology, enabling the convergence of advanced communication, precise sensing and localization, artificial intelligence (AI) and computing technologies.
- Cost efficiency: One early learning from deploying 5G networks is that many new technologies can be expensive to roll out broadly. Today, mobile operators are looking for ways to reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) of their networks. Reducing network energy consumption can optimize operational cost, but to save on capital expenditure, a software-centric system with network APIs can allow mobile operators to leverage their 5G investment.
- Societal equity: 6G will continue to foster digital inclusion, enabling cost-effective technologies that can broadly deliver 6G access to bridge the digital divide. New 6G technologies can promote quality of life improvements, with democratized access to public services such as healthcare, education and public safety.
- Environmental sustainability: A common theme across the different global 6G visions is for it to promote a greener future. This anchors both in efficient 6G network operations (i.e., energy savings, eco-friendly deployment footprint) as well as more sustainable vertical industries (e.g., smart transportation, precision agriculture and more).
- Trust and reliability: The cellular evolution has consistently emphasized the importance of security and privacy, with each generation aiming to enhance trustworthiness. As we look towards 6G, it's anticipated to uphold this legacy by integrating cutting-edge technologies such as quantum-safe communications and AI-driven security.
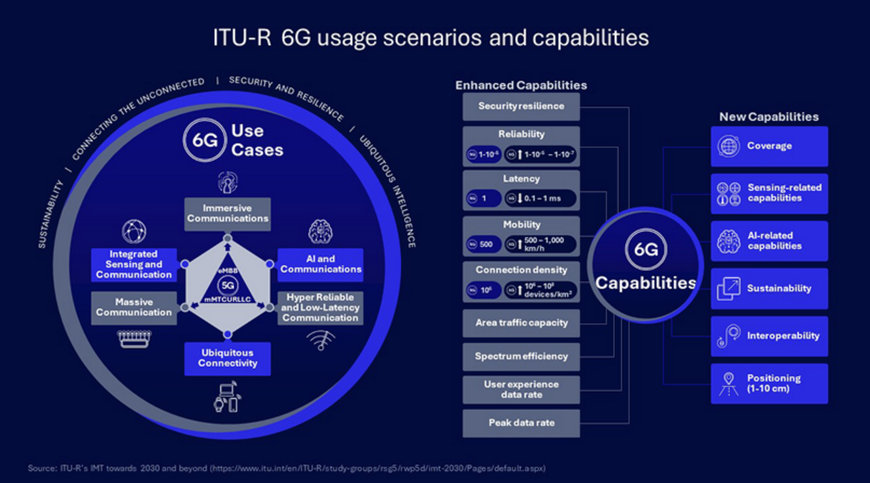
6G use cases and capabilities
The 6G technology platform is expected to take a significant leap forward, supporting enhanced system capabilities that go beyond communication. The IMT-2030 framework defined by ITU-R sets the initial vision for this advancement, outlining key usage scenarios and performance metrics that should shape the target for future wireless technologies.
As these technologies develop, 6G is anticipated to integrate AI, advanced computing, and system resilience features, alongside innovative green technologies and integrated sensing and communications (ISAC), marking a new converging era of the physical-digital-virtual worlds.
- Immersive experiences: 6G will take extended reality (XR) to brand new levels, enabling lightweight devices that can be deployed at the same scale of today’s smartphones. New capabilities like digitization of multisensory aspects (e.g., such as human senses of touch, smell, sight, taste), enhanced sensor fusion and brain-computer interface can deliver hyper-realistic experiences (e.g., holographic teleportation). Another focus is to also enable live and interactive immersive content creation and delivery.
- Digital twins: the modeling of a physical system in the digital domain can be used to enable new efficiencies and use cases, including the communications network and more. Along with rapid advancements of AI, 6G digital twins is poised to bring enhanced security and privacy, predictive and prescriptive insights, as well as many others.
- Smart industry and robotics: 5G established the technical foundation for high-performance industrial IoT (e.g., URLLC, TSN), and 6G targets to unleash the full potential of next-generation robotics, including delivery robots, service robots, as well as autonomous and collaborative robots that can work in tandem with humans in this highly integrated and automated environment.
- Fixed wireless access (FWA): 6G brings an opportunity to revolutionize broadband services. With the allocation of new wide-area spectrum (e.g., upper mid-band), 6G can enable high network capacity and improved cost-efficiency, extending coverage across urban, suburban and rural regions alike, fostering greater inclusivity and connectivity.
- Next-generation internet of things (IoT): It's important that 6G can efficiently support lower-complexity devices from the very start. From low-power, wide-area (LPWA) to ambient IoT devices (i.e., powered by energy harvesting with/without storage), 6G is envisioned for diverse vertical services in healthcare, automotive, agriculture and more.
- Connected transportation: 6G brings the opportunity of next-level transportation safety and experiences. Through new 6G capabilities like ISAC, the 5GAA consortium envisioned the next-generation network to enable real-time environmental modeling, intelligent automated driving systems and enhanced in-vehicle experiences.
- Critical communications: 6G is tasked to deliver the next level of trust, reliability and security in mobile communications. This is especially important for those use cases that are mission-critical, such as public safety communications. 6G needs to leverage the learning and deployment from 5G to enable ubiquitous coverage and more.
- Other emerging deployments and use cases: It's expected that many of these 6G use cases would leverage seamless multi-connectivity solutions spanning terrestrial and/or non-terrestrial communications to deliver services. And of course, we are only in the very early chapter of the 6G technology cycle. As we stand on the brink of these advancements, it's clear that the future holds use cases that will surpass our current imagination.
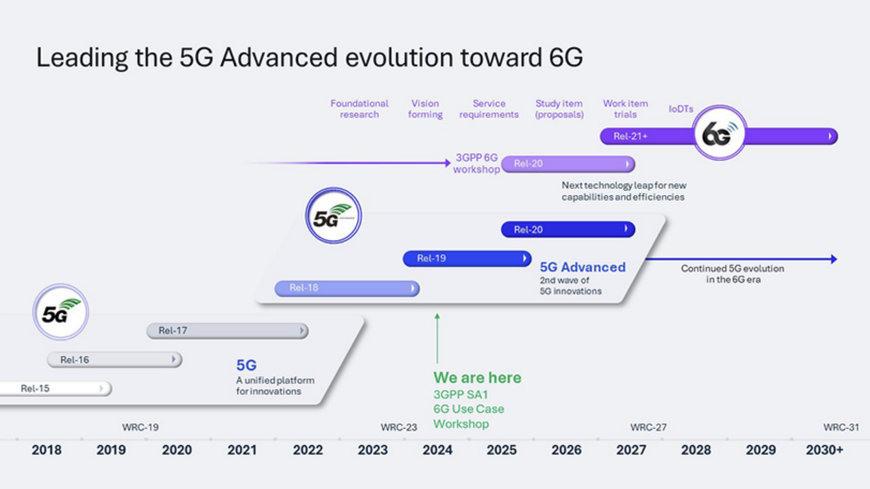
What’s next?
Qualcomm Technologies' vision for the future of wireless technology is continuous and expansive. With the evolution of 5G Advanced, the foundation for 6G is being laid, promising to bring a new era of technological advancements. The focus is not only on enhancing wireless designs but also on integrating a broader range of technologies to enable intelligent computing everywhere. The anticipation of 6G includes the potential for groundbreaking developments in wireless communication, AI, computing, RF sensing and network resiliency, setting the stage for a smarter, more sustainable wireless platform of our future.

