electronics-journal.com
19
'22
Written on Modified on
COP26 Session: How Much Can Electronic Components Contribute to CO₂ Reduction in Finished Products?
At COP26 (the 26th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) held in 2021, TDK was a featured speaker at an off-site session organized by Hitachi, Ltd. about its procurement partners. There, TDK presented its ongoing initiatives to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions in its supply chain.

Quantifying the reduction of CO₂ in the use stage of electronic components
In November 2021, COP26 (26th Conference of the Parties) was held in Glasgow, U.K., where the 197 countries party to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) met to discuss climate change. Contemporaneously, at an online session hosted by Hitachi—a COP26 Principal Partner—TDK was recognized for its company-wide efforts in recent years to bolster its climate change initiatives and environmental policies as well as for its efforts to cut emissions of CO2 from the use of its products, and was featured as an innovative example of such activities. At the session, TDK gave a presentation on Activities to Quantify the Reduction of CO2 Emissions of our Electronic Components in the Use Stage.
Tetsuya Kuwashima, General Manager of TDK Corporation’s Safety & Environmental Group, Sustainability Promotion Headquarters, explained the significance of TDK’s environmental initiatives during the session. “As an electronic components manufacturer, TDK believes it is essential to create mechanisms to identify and reduce CO₂ emissions throughout the entire supply chain. Guided by principles the company has followed since its founding, TDK has been continually engaged in the reduction of CO₂ related to the use of its products in society as a priority matter.”
Product Contribution, an original TDK concept
Since 2011, TDK has championed the concept of Product Contribution and has been engaged in efforts to evaluate and calculate the energy-saving effect of its products. Back then, the environmental activities of electronic component manufacturers were predominantly concerned with easing the impact of their own activities. By 2016, TDK had formulated TDK Environmental Vision 2035—a group-wide environmental plan—actively seeking to reduce the environmental impact across the entire lifecycle of its products, including the procurement, development, manufacturing, transportation, use and disposal stages.
The electronic components that TDK develops and manufactures cut energy consumption by minimizing excess heat generation and noise, and their miniaturization helps reduce CO₂ emissions in finished products. However, it had been difficult to verify the effectiveness of these efforts quantitatively. Kuwashima described the methodology used to calculate the reduction of CO₂ in the product use stage.
“We refer to the degree to which electronic components contribute to reducing CO₂ emissions during product use in a finished product as Product Contribution. To calculate the amount of CO₂ reduced during use, we first calculate the energy savings of the new product relative to a benchmark product. Next, we multiply that reduction by a conversion factor corresponding to CO₂, and finally by the sales volume of the component to derive the total amount of CO₂ eliminated. TDK has established guidelines for this method, which have also been validated by a third-party organization.”
How Product Contribution is calculated
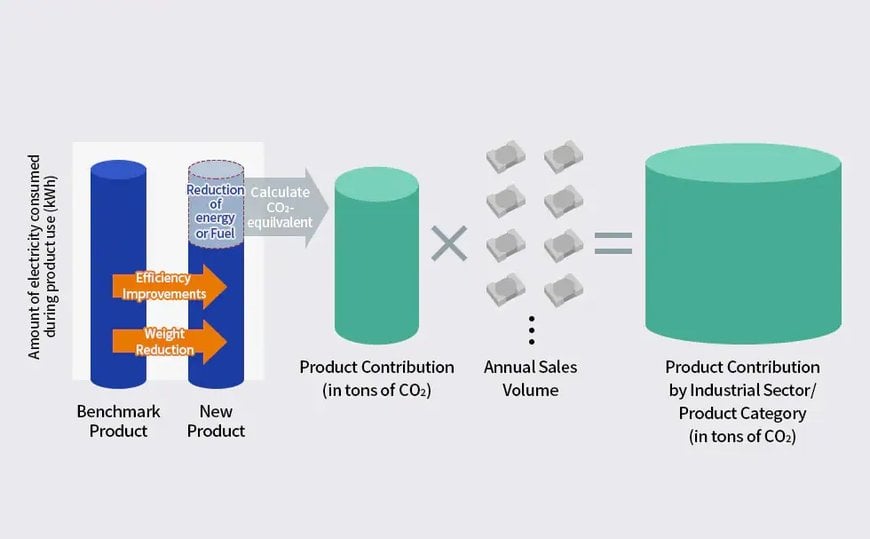
The concept of Product Contribution: By calculating the amount of CO₂ reduced through efficiency improvements and weight reduction in energy-saving products, and multiplying them by annual sales volumes, the amounts contributed to the reduction of CO₂ can be broken down by industrial sector and by product group.
2.63 million tons of CO₂ slashed annually
TDK calculates the amount of CO₂ reduced through electronic components in finished products for each industrial sector using the method described above. “In 2020, 253,000 tons of CO₂ were slashed in the automotive sector through the miniaturization of electronic components. Higher efficiencies and reduction of excess heat and noise cut 846,000 tons in the information and communication technologies sector and 1.53 million tons in the industrial equipment and home appliances sector. In total, 2.63 million tons of CO₂ have been reduced, equivalent to 26% of emissions in the use stage in what we refer to as Scope 3,” Kuwashima continued.
TDK has been increasing its CO₂ reductions every year since it began these activities in 2011. In the 2020 fiscal year, reductions almost doubling those of 2014 were achieved.
Amount of CO₂ Reductions by Industrial Sector (FY 2020 Results)

In the 2020 fiscal year, a reduction of approximately 2.63 million tons of CO₂ emissions was achieved through miniaturization of electronic components and reduction of excess heat and noise.
Kuwashima spoke about the challenges facing Product Contribution in the future. “TDK has been calculating the amount of CO₂ emissions reduced in the use stage of products, endeavoring to lessen CO₂ emissions in society. To achieve carbon neutrality in the future, we believe it is critical to share information externally on how emissions are calculated, manage it across all of Scope 3 (raw materials procurement, manufacturing, transportation, sales, and disposal), and address the issue in the supply chain as a whole.”
The Impact of Technical Initiatives on the Product Lifecycle
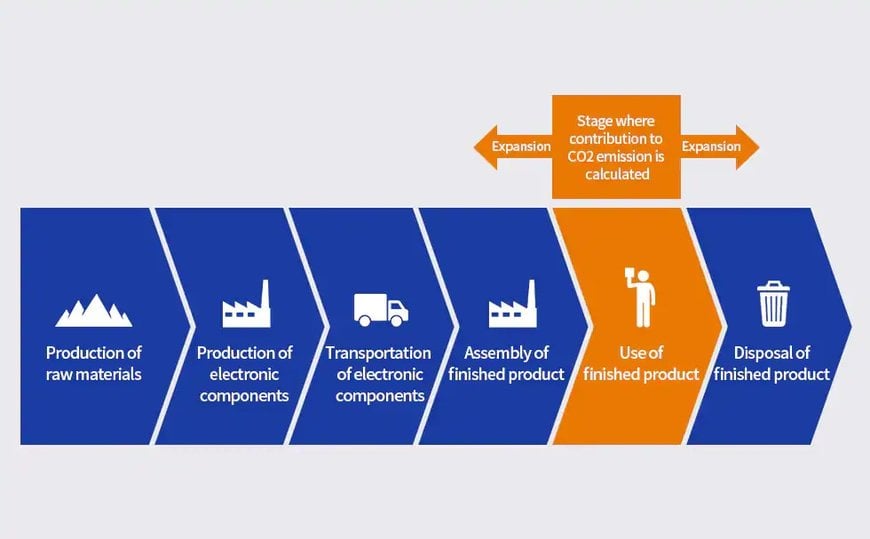
While current activities focus on calculating the amount of contribution by TDK’s electronic components to reducing CO₂ emissions during the use of finished products, expanding the scope of calculations to include lifecycle stages such as raw materials procurement and disposal is being planned.
www.tdk.com

