electronics-journal.com
10
'21
Written on Modified on
NEW 5TH GEN P-CHANNEL MOSFETS DELIVER CLASS-LEADING LOW ON RESISTANCE
Broad 24-model lineup with withstand voltages of -40V/-60V ideal for large consumer and industrial equipment.

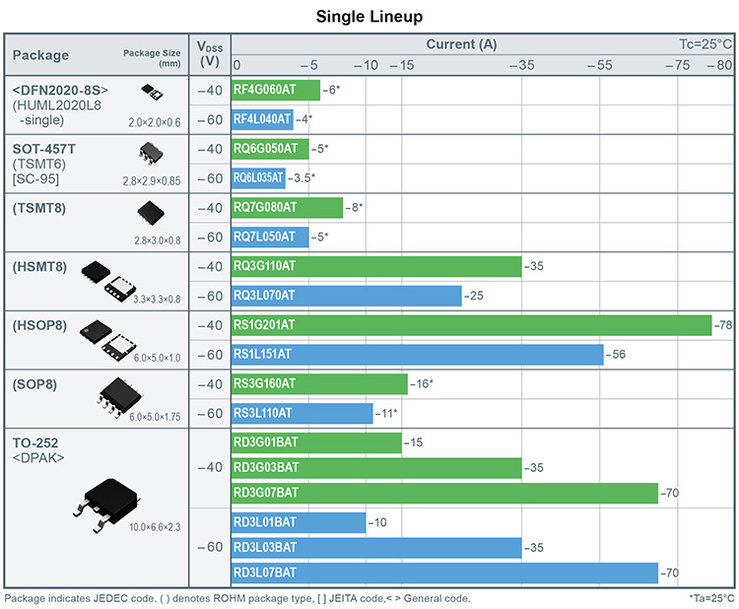
ROHM releases a 24-model lineup of 24V input, -40V/-60V withstand voltage P-channel MOSFETs available in both single (RQxxxxxAT/RDxxxxxAT/RSxxxxxAT/RFxxxxxAT) and dual configurations (UTxxx5/QHxxx5/SHxxx5) – ideal for industrial and consumer applications such as factory automation, robotics, and air conditioning systems.
HSOP8 and DFN2020-8D package
In recent years, as demand for higher efficiency and power density drives adoption of higher input voltages in industrial and consumer applications, MOSFETs are expected to provide not only low ON resistance, but high withstand voltages as well.
Two types of MOSFETs exist: N-channel and P-channel. Although N-channel types generally feature higher efficiency, when used in the high side a gate voltage higher than the input voltage is needed, complicating circuit configuration. On the other hand, P-channel MOSFETs can be driven with a gate voltage lower than the input voltage, simplifying circuit configuration considerably while reducing design load.
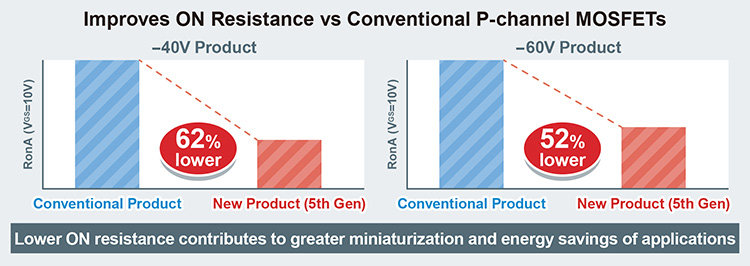
Against this backdrop, ROHM developed low ON resistance -40V/-60V P-channel MOSFETs compatible with 24V input utilizing advanced 5th gen refined process. Based on ROHM’s market-proven P-channel MOSFET structure, these new products leverage refined process technology to achieve the lowest ON resistance per unit area in their class. This translates to 62% lower ON resistance vs conventional products for -40V new products and 52% for the -60V new products.
At the same time, quality is improved by optimizing the device structure and adopting a new design that mitigates electric field concentration. As a result, both high reliability and low ON resistance (which are typically in a trade-off relationship) are achieved. These solutions contribute to stable long-term operation in industrial equipment demanding exceptional quality.
ROHM continues to develop a variety of packages for a wide range of applications, including products optimized for the automotive sector. In addition to these 5th gen P-channel MOSFETs, to strengthen our lineup for 5G base stations and data center servers, where demand is growing, we are developing higher efficiency N-channel MOSFETs. These products contribute to reducing application design load while increasing higher efficiency and reliability.
Key Features
1. Class-leading low ON Resistance
These new products utilize ROHM’s 5th gen refined process to achieve a finer gate structure and higher current density than ROHM’s conventional products, resulting in the class-leading low ON resistance per unit area for 24V input -40V/-60V withstand P-channel MOSFETs. 62% lower ON resistance vs conventional products for -40V new products and by 52% for the -60V new products contribute to greater energy savings and miniaturization.
2. New design improves quality
The new lineup leverages accumulated expertise regarding reliability to optimize the device structure while adopting a new design that mitigates electric field concentration at the gate trench corner where the electric field is most concentrated. This allows ROHM to succeed in improving reliability against degradation of element characteristics at high temperature bias without sacrificing ON resistance, which is typically in a contradictory relationship, contributing to stable long-term operation in industrial equipment that demand superior quality.
3. Expanded lineup improves reliability while reducing design load in a wide range of applications
The 24-model lineup is offered in withstand voltages of -40V/-60V ideal for factory automation, robotics, and commercial air conditioning systems. Going forward, ROHM will continue to develop a variety of packages that support application other than industrial equipment, including products optimized for the automotive sector. In addition to P-channel MOSFETs, we are developing N-channel types utilizing next-gen processes that adopt a new structure designed to improve reliability and reduce application design load.
Terminology
MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) The most commonly used structure in FETs. Often adopted as switching elements.
P-channel/N-channel MOSFETs
P-channel MOSFET: A type of MOSFET that conducts when a negative voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source. This allows it to be driven with a voltage lower than the input voltage, simplifying circuit configuration.
N-channel MOSFET: A type of MOSFET that conducts when a positive voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source. The smaller drain-source ON resistance compared with P-channel MOSFETs results in lower steady state loss.
ON Resistance
The resistance value between the Drain and Source of a MOSFET during operation. The smaller this value is, the lower the (power) loss during operation.
Trench Structure
The word ‘trench’ means a narrow excavation or groove. This design involves forming a groove on the chip surface and the gate on the MOSFET side wall. Unlike planar MOSFETs, no JFET resistance exists, making it possible to achieve a finer structure.
www.rohm.com

