What You Should Know About RFID Tags
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags are used for asset recognition through digital encoding technology. These tags use an antenna, an electronic chip, or an integrated circuit to send and receive data. Written by Y. Belgnaoui.

RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology operates through a radio wave exchange between a reader and the tag, which contains a chip and an antenna. The reader emits a radio signal that the tag’s antenna captures to activate it. The tag’s chip, powered by this signal, then transmits the stored information (such as a serial number or tracking data) back to the reader, enabling contactless and remote identification.
The RFID tag market is segmented by tag type, frequency band used, and targeted application. There are two main categories of RFID tags: active and passive. The key difference between a passive and an active RFID tag lies in their power source. Passive tags have no battery. They are powered by the electromagnetic field generated by the reader, which limits their read range to a few centimeters up to about ten meters. Active tags, on the other hand, contain a built-in battery that enables them to transmit their own signal. As a result, they offer a much longer reading range, often several dozen meters, reaching up to 100 to 150 meters.
Tags can operate on low frequency (125 kHz to 134 kHz), high frequency (13.56 MHz), and ultra-high frequency (850–960 MHz). The frequency directly impacts detection range and reading speed, as well as the ability to read through materials and handle radio signal collisions. High frequencies (UHF) provide longer range but are more sensitive to metal interference, whereas low frequencies penetrate materials more effectively and offer greater precision for close-range reading.
RFID tags are specifically tailored to several industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, animal tracking, retail, healthcare, logistics and supply chain, security and access control, transportation, and more.
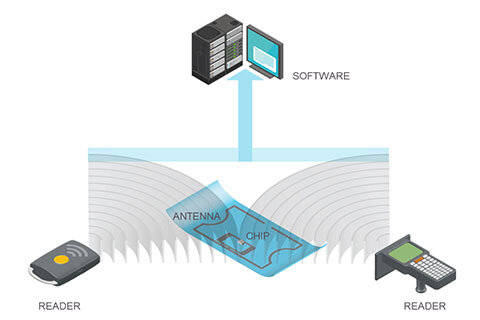
The data stored on an RFID tag is read by a dedicated reader and transmitted to specialized software for processing. (Source: Murata).
According to a study on the RFID tag market published by Allied Market Research, the RFID tag market has experienced significant growth in recent years due to increasing demand across multiple sectors. This growth is largely attributed to the need for better inventory management, enhanced supply chain visibility, and optimized asset tracking systems.
The adoption of RFID technology in sectors such as manufacturing and logistics has played a major role in the expansion of the RFID tag market. RFID tags provide real-time visibility of goods across the entire supply chain. This tracking capability improves process efficiency, increases productivity, and reduces operational costs. In the manufacturing sector, RFID tags are used to monitor components and finished products, reinforcing stock control and optimizing quality management processes. These markers also improve shipment tracking and enable more accurate deliveries, thereby reducing the risk of loss or misplacement in logistics operations.
However, RFID tag performance can be affected by environmental factors. For example, metallic interference can disrupt radio wave transmission, which is critical to RFID functionality—especially in metal-heavy environments. Liquids, particularly water, can absorb radio waves and reduce tag performance in humid or liquid-rich areas. Additionally, extreme temperatures can damage the electronic components of RFID tags or shorten battery lifespan. To overcome these challenges, more robust and specialized RFID solutions may be required. These are often more complex and costlier.
The integration of sensors into RFID tags represents a major advancement. This evolution allows RFID tags not only to locate and track objects but also to collect and share additional data such as temperature, atmospheric pressure, and humidity levels. This is a significant advantage in sectors like logistics and supply chain management, where monitoring sensitive products—especially perishable goods or healthcare items—is essential during storage and transport.
RFID tags equipped with sensors can also deliver real-time information on the operation of production machinery, helping to ensure their proper functioning. In agriculture, these tags can detect environmental parameters, making crop management easier. The integration of sensing capabilities into RFID tags positions them as highly effective tools for advanced data collection and analysis.

