TDK About The rapid adoption of wireless earphones and the technical challenges they face
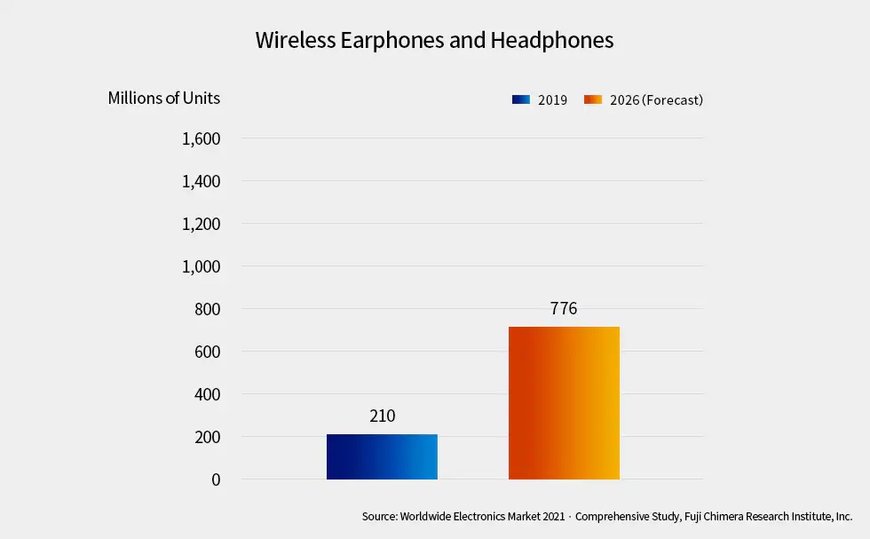
The market for wireless earphones and headphones is rapidly expanding worldwide. According to the 2021 Worldwide Electronics Market published by Fuji Chimera Research Institute, it is estimated to have reached 210 million units in 2019 and forecasted to grow to 776 million in 2026 (approximately 3.6 times the 2019 level). A driving factor is the advent of completely wireless earphones (TWS: True Wireless Stereo*1), where the left and the pieces are independently wireless.
The primary advantage of TWS is that it eliminates the hassle of wires. You can enjoy music while commuting to work or school, or engaging in sports, housework or shopping—more comfortably than with the conventional wired type. In the future, TWS will not only be used for listening to music or as a smartphone accessory—it is expected to become a hearable*2 that will change our lives and society. Hearables, as they are called, are computers worn on the ear: wearable devices that focus on voice input and output. Hands-free calling, biometric monitoring and simultaneous interpretation are among the anticipated applications.
The global market for wireless earphones/headphones
For TWS to continue evolving into the future, achieving better sound and smaller size are essential. While TWS and other wirelessly-equipped audio devices have brought us convenience, they are inherently plagued by one structural problem: wireless signals can infiltrate into audio signals as noise, manifesting themselves as audible buzzes. Suppressing this noise as much as possible is paramount to achieving high-fidelity sound.
To make things more challenging, TWS—unlike its wired siblings—requires the antennas and batteries to be housed within the earpieces, limiting the space to place amplifiers and for drivers to vibrate. This leads to larger enclosures and inferior sound quality, engendering demand for smaller circuitry and fewer components.
Unique notch filter solution with ESD protection enables miniaturization and superior sound quality
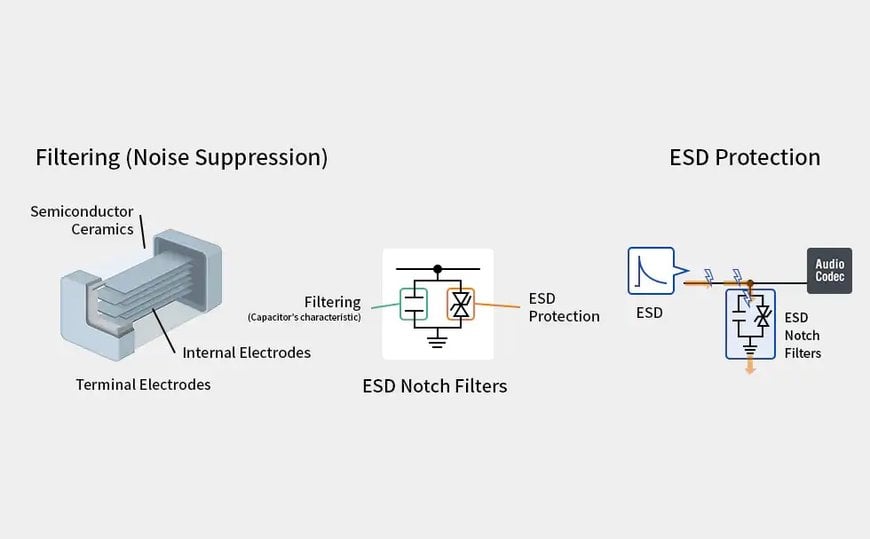
Given this background, TDK has developed the AVRF series of notch filters with built-in ESD protection. A notch filter is a component that removes noise by blocking signals at specific frequencies, such as those used for wireless communications.
Thanks to its unique material and structural design, the AVRF series offers excellent attenuation characteristics*3 for specific frequencies. It suppresses noise and improves reception sensitivity for TWS and other wireless communications, contributing to superior sound quality.
With and without TDK’s filter
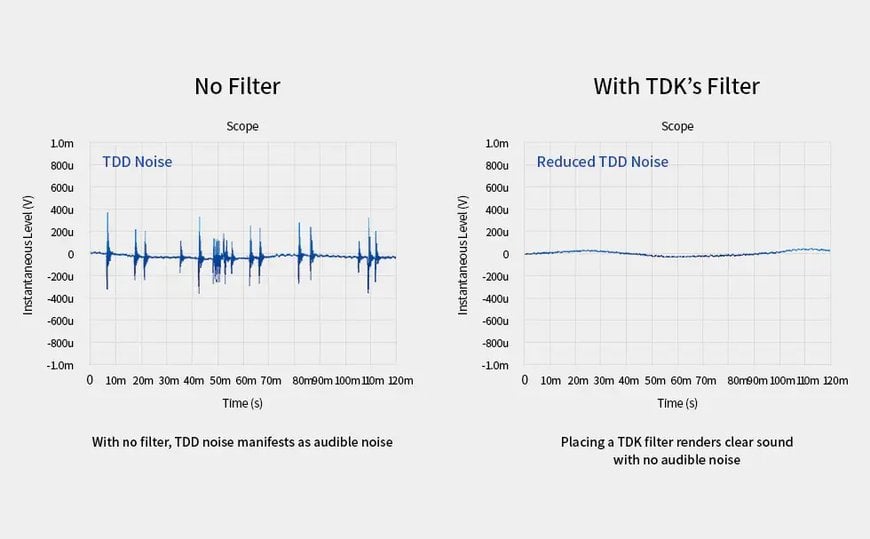
An additional strength is its built-in ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)*4 and surge protection feature. ESD is the discharge of static electricity that occurs when an electrically charged object like the human body comes into contact with an electronic device. Because wireless audio devices and other electronics are routinely handled by human hands, they require ESD protection.
A component called a TVS diode*5 is commonly used to protect electronic devices from ESD. While it provides ESD protection, a TVS diode is ineffective as a noise countermeasure, necessitating another component like an MLCC. The AVRF series integrates filter (noise suppression) and ESD protection functionalities by leveraging TDK’s proprietary multilayer process and material technologies. Both noise and ESD countermeasures can be implemented using a single chip, eliminating the need for TVS diodes—which are larger than notch filters—enabling a significant reduction in circuit size.
Noise and ESD countermeasures on a single chip
Ideal for audio equipment designed for high fidelity
Katsuyuki Takei, Manager at TDK’s Piezo & Protection Devices Business Group, spoke about the future prospects of the AVRF series. “The AVRF series of notch filters are ideal as EMC (electromagnetic compatibility)*6 measures not only for TWS but for audio circuits in devices like smartphones and smart speakers. Implementing EMC countermeasures implies that devices can establish a noise-resistant environment. As wireless and communication devices are expected to connect everything in the future, noise countermeasures will grow ever more crucial. Presently, the AVRF series primarily targets audio equipment for wireless communications, but we hope to expand its scope to include automobiles, industrial equipment, energy and healthcare.”

Katsuyuki Takei
Manager
Multilayer Products Section
Semiconductor Material Products Division
Piezo & Protection Devices Business Group
TDK Corporation
Through its notch filters, TDK will continue to provide optimal solutions for high fidelity audio equipment, underpinning the communication networks of the future.
Noise and ESD protectionfor audio devices featuring wireless communications
The AVRF series of notch filters with built-in ESD protection
The lineup includes products that cover the 2.4, 5GHz bands used for Bluetooth and Wi-Fi and the cellular bands (700MHz to 2.7GHz), and for noise suppression in class-D amplifiers. For details, please visit the Product Center.
Terminology
- Wireless headphones/earphones: Two types exist: the completely wireless (True Wireless Stereo) type, where the left and right sides are completely independent; and the integrated (Semi-Wireless) type, where the two sides are connected by a cable.
- Hearable devices: Computers and terminals that can be worn on the ear, as well as wireless earphones with built-in voice assistant functions, are collectively referred to as hearables.
- Attenuation characteristics: Numerical values indicating the effectiveness of reduction across a spectrum of frequencies in a filter circuit.
- ESD: Abbreviation for Electrostatic Discharge. A typical example of ESD is static electricity that builds up in a human body when walking on a carpet and is discharged when metal or other objects are touched. ESD is generally in several thousand volts, and can cause serious damage to electrical circuits.
- TVS Diode: A Transient-Voltage-Suppression (TVS) diode protects voltage-sensitive components from electrostatic discharges (ESDs).
- EMC: Abbreviation for Electromagnetic Compatibility. It refers to a combination of the concepts of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS).

