electronics-journal.com
08
'20
Written on Modified on
Advanced Light-Receiving Technology from Toshiba Enables Solid-State LiDAR Free from Reliance on Mechanical Components
Compact, low-cost and simple to install solution is suitable for wide variety of vehicle types.
Addressing the ongoing migration towards autonomous driving, Toshiba (TOKYO: 6502) has announced the introduction of a high-resolution, long-range light-receiving technology for deployment in solid-state LiDAR systems. By removing the need for bulky mechanical components, the technology realizes cost and space savings and enhances operational reliability. At its heart is Toshiba’s proprietary compact, high-efficiency silicon photo-multiplier (SiPM).
In general, SiPM are suitable for long-range measurement as they are highly light sensitive. However, the light-receiving cells composed on SiPM require recovery time after being triggered, and in strong ambient light condition they also need a large number of cells, since they must have reserve cells to react to reflected laser light.
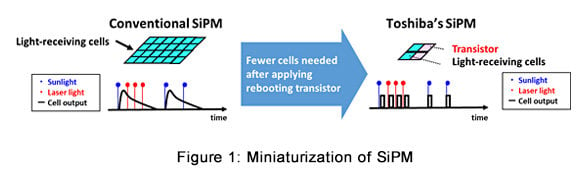
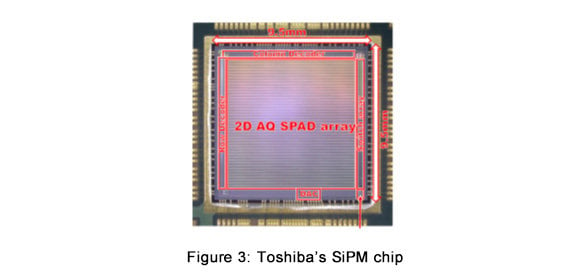
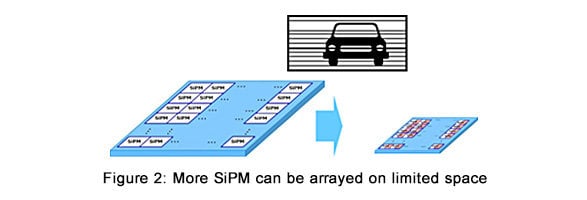
Toshiba’s SiPM applies a transistor circuit that reboots the cells to reduce the recovery time. The cells function more efficiently and fewer are needed, securing a smaller SiPM, as shown in Figure 1. This realizes a higher-resolution SiPM array while maintaining high sensitivity, as shown in Figures 2 and 3.
Current LiDAR systems require mechanical components to continuously rotate the laser emitters and their accompanying optical detection devices. Utilizing solid-state LiDAR instead secures numerous operational advantages—and Toshiba’s ground-breaking SiPM innovations are making this possible. Field trials with a LiDAR prototype, shown in Figure 4, using commercially available lenses, from wide-angle to telephoto lenses, have demonstrated the system’s effectiveness over a maximum distance of 200m (Figure 5). This effectively quadruples the capabilities of currently available solid-state LiDAR systems while maintaining high resolution.
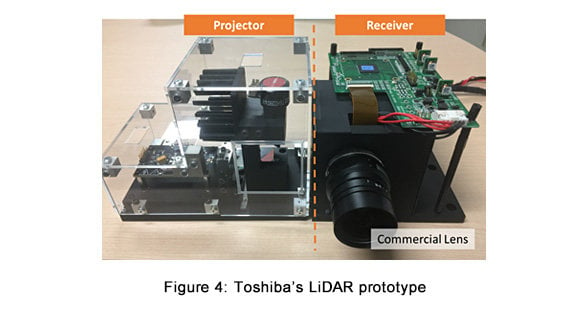
Furthermore, Toshiba’s LiDAR system can easily be built with commercial lenses, which eliminates complex customization and allows it to be applied in a wide variety of self-driving vehicles. The technology’s inherent compactness allows placement in multiple locations on vehicles that had previously presented a major challenge; and it will also broaden LiDAR applications outside of the automotive sector.
Toshiba will continue R&D to further extend LiDAR measuring range, raise resolution and advance miniaturization, with the target of practical use of the SiPM in FY2022.
www.toshiba.co.jp

